For those who are new to smart boards, the configuration details can be quite overwhelming. Terms like infrared touch versus capacitive touch, 4K HD resolution, and choosing the right screen size for your needs can leave many confused. When a smart board supplier presents the specifications, it often raises many questions. What size is best suited for your space? How do the different touch technologies affect the user experience? Which resolution will give you the clearest display? These are just some of the considerations you’ll need to address. Today, we’ll break down the key specifications of interactive smart boards to help you understand and make an informed choice. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Screen Size and Resolution
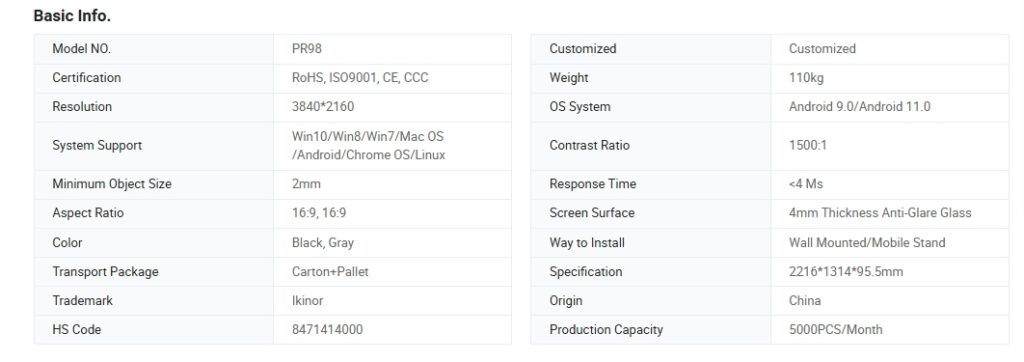
When selecting a smart board, choosing the right screen size is essential to ensure visibility and usability in your space. Common options include 65-inch, 75-inchy 86-inch screens, which are popular for classrooms, conference rooms, and smaller offices. However, for larger spaces, such as meeting rooms over 100 square meters, a 100-inch screen may be a better option. A larger screen ensures that everyone in the room can see the content clearly, especially in a larger environment where visibility from a distance can be challenging. Check Article: Smart Board Dimensions: How To Choose
Along with screen size, resolution plays a crucial role in the overall clarity and detail of the display. The most common resolution types are HD (High Definition) and 4K (Ultra High Definition). HD resolution offers a good level of clarity for general use, but for high-definition visuals, intricate details, or large audiences, 4K resolution is preferred. 4K provides four times the pixel count of HD, delivering sharper, crisper images and smoother text, which is especially important for presentations, video conferencing, and digital content creation.
Choosing the appropriate resolution depends on your needs and the size of the display. For smaller boards (65-inch), HD may suffice, but for larger screens (75-inch and above), 4K is recommended for the best clarity. This ensures that content remains clear, whether you’re displaying text, images, or videos, and that every detail is visible to everyone in the room.

Touch Technology and Sensitivity
When choosing a smart board, understanding the touch technology is crucial for a seamless user experience. The two most common types of touch technology used in smart boards are capacitive touch and infrared touch, each offering unique benefits.
Capacitive touch technology uses the electrical properties of the human finger to register touch, making it highly responsive and accurate. It allows for a smooth and precise touch experience, supporting multi-touch capabilities, which means multiple users can interact with the board simultaneously. Capacitive touch boards are ideal for environments where precision is essential, such as detailed presentations or design work.
On the other hand, infrared touch technology uses infrared sensors to detect touch on the screen. These sensors create an invisible grid of light beams, which break when the screen is touched. While infrared touch can be less responsive than capacitive touch, it tends to be more durable and works well with gloved hands or styluses. It is also generally more cost-effective, making it a good option for budget-conscious buyers.
Multi-touch capability refers to a board’s ability to recognize and respond to multiple touchpoints at the same time. Both capacitive and infrared technologies offer multi-touch features, but capacitive touch generally provides better responsiveness. The sensitivity of the board is important for ensuring smooth interaction, whether it’s for writing, drawing, or navigation. To learn more about the differences between touch technologies, check out this article on capacitive vs. infrared touch.
Connectivity and Compatibility
When choosing a smart board, connectivity and compatibility are essential factors to ensure seamless integration with your devices and software. One of the key aspects to consider is the range of available ports on the smart board. Common ports include HDMI, USB, and VGA. HDMI ports allow you to connect external devices like laptops, projectors, and media players, providing high-quality video and audio output. USB ports are used to connect peripherals like keyboards, mice, or external storage devices, making it easy to expand the functionality of your smart board.
Wireless connectivity options such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are also important for wire-free interaction. Wi-Fi allows you to connect the smart board to your network, enabling features like web browsing and screen mirroring from other devices. Bluetooth is often used for connecting smaller devices like speakers, mice, or mobile phones for more interactive functionality without the need for cables.
Operating system compatibility is another key consideration. Most smart boards are designed to work with Android or Windows operating systems. If you plan to use both operating systems on the same smart board, you will need an OPS (Open Pluggable Specification) computer. An OPS computer acts as an external module that allows the board to switch between multiple operating systems, ensuring full compatibility with both Android and Windows applications. This is an important feature for businesses or educational environments that require flexibility in their tech setup.

Audio and Video Features
Audio and video features are crucial components to consider when selecting a smart board, as they directly impact the quality of presentations, meetings, and interactive sessions. One important aspect to evaluate is whether the smart board has built-in speakers or if an external audio system is needed.
Built-in speakers offer convenience, as they eliminate the need for additional equipment. Many smart boards come with integrated audio systems that provide clear sound for most environments, especially in small to medium-sized rooms. However, for larger spaces or environments with high ambient noise, external audio systems might be necessary to ensure optimal sound distribution and volume.
When it comes to video output, smart boards typically offer options to connect to external displays or projectors. This is particularly useful if you want to share content across multiple screens in large conference rooms or classrooms. Common video output options include HDMI and VGA ports, which allow you to connect the smart board to other devices like projectors or external monitors. Some advanced smart boards also support wireless video streaming via Wi-Fi, allowing you to mirror content from other devices without the need for physical cables.
Choosing the right audio and video setup depends on your space’s size and acoustic needs. Ensuring that the smart board can easily connect to external systems will provide flexibility and enhance the overall multimedia experience.

Software and Interactive Features
Software and interactive features play a significant role in maximizing the functionality of a smart board. Many smart boards come with pre-installed apps, such as whiteboard and collaboration tools, which are essential for engaging presentations and teamwork. The built-in whiteboard app is often free for lifetime use, offering a convenient and cost-effective solution for users who need basic drawing, annotation, and collaboration features. However, some advanced whiteboard apps might require a separate license or subscription. It’s important to check with the supplier whether the whiteboard app is included for free or if an additional cost will be incurred for premium features.
In addition to whiteboard tools, many smart boards also offer other interactive applications like video conferencing tools, document sharing, and annotation features. These apps enable seamless collaboration, whether you’re in an educational setting, a business meeting, or a creative brainstorming session.
Support for third-party applications and software integration is another important feature to consider. The best smart boards are compatible with various external software and tools, such as Microsoft Office, Google Drive, and video conferencing platforms like Zoom or Microsoft Teams. This ensures that users can integrate the smart board with their existing technology infrastructure without compatibility issues. Before making a purchase, ask the supplier about the board’s software compatibility and integration capabilities to ensure it meets your specific needs.
Durability, Maintenance, and Support
Durability, maintenance, and support are crucial factors when selecting a smart board, as they ensure long-term usability and smooth performance. One of the key considerations is the screen protection features. Smart boards typically come with anti-glare and scratch-resistant screens to protect against everyday wear and tear. Anti-glare technology reduces reflections and enhances visibility, especially in brightly lit environments, ensuring that content is always easy to see. Scratch-resistant screens, on the other hand, protect the display from physical damage, maintaining clarity and preventing the accumulation of scratches over time.
Warranty and technical support options are essential for ensuring that your investment is protected. Most reputable smart board suppliers offer a warranty, which covers potential defects and provides peace of mind. It’s important to verify the details of the warranty, including its duration and the type of coverage it offers. Additionally, reliable technical support is a must. Look for suppliers who provide prompt assistance through multiple channels, such as phone, email, or live chat, and who offer a comprehensive troubleshooting guide for quick fixes.
Ease of software updates and troubleshooting is another critical aspect. A smart board should support software updates that are easy to install and do not disrupt the user experience. Suppliers that offer a Device Management System (DMS) provide added value. With DMS, users can monitor and manage multiple devices in real time, which is especially beneficial for classrooms or office environments. This feature helps ensure efficient control, smooth operations, and organized management of smart board devices, enhancing the overall user experience.





